Spectacular Info About What Is The Formula To Scale A Line Excel How Change Axis Values
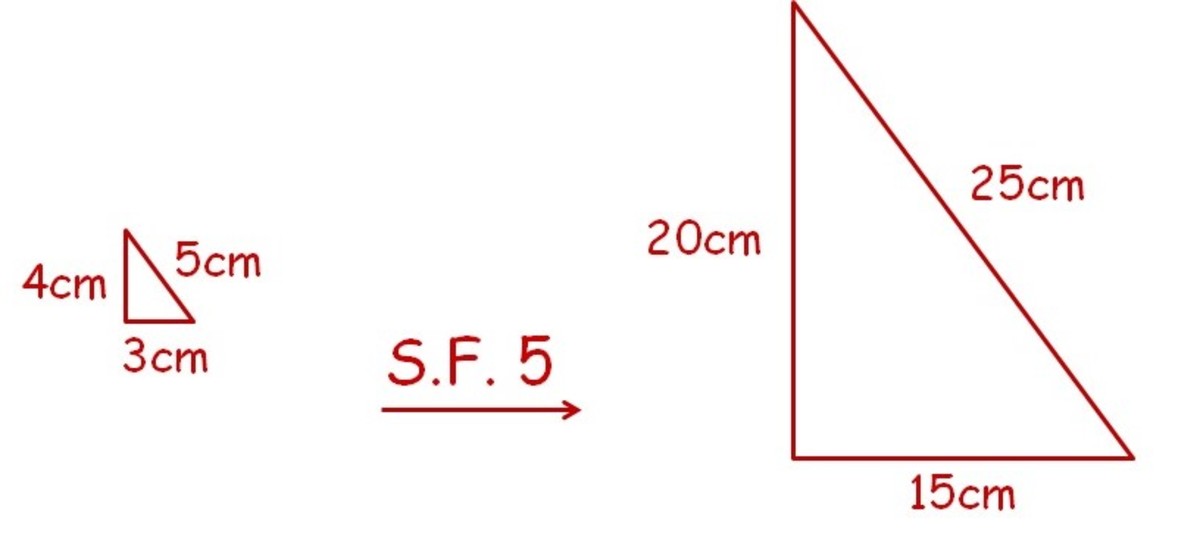
Learn the scale factor definition and how to find the scale factor of similar figures.
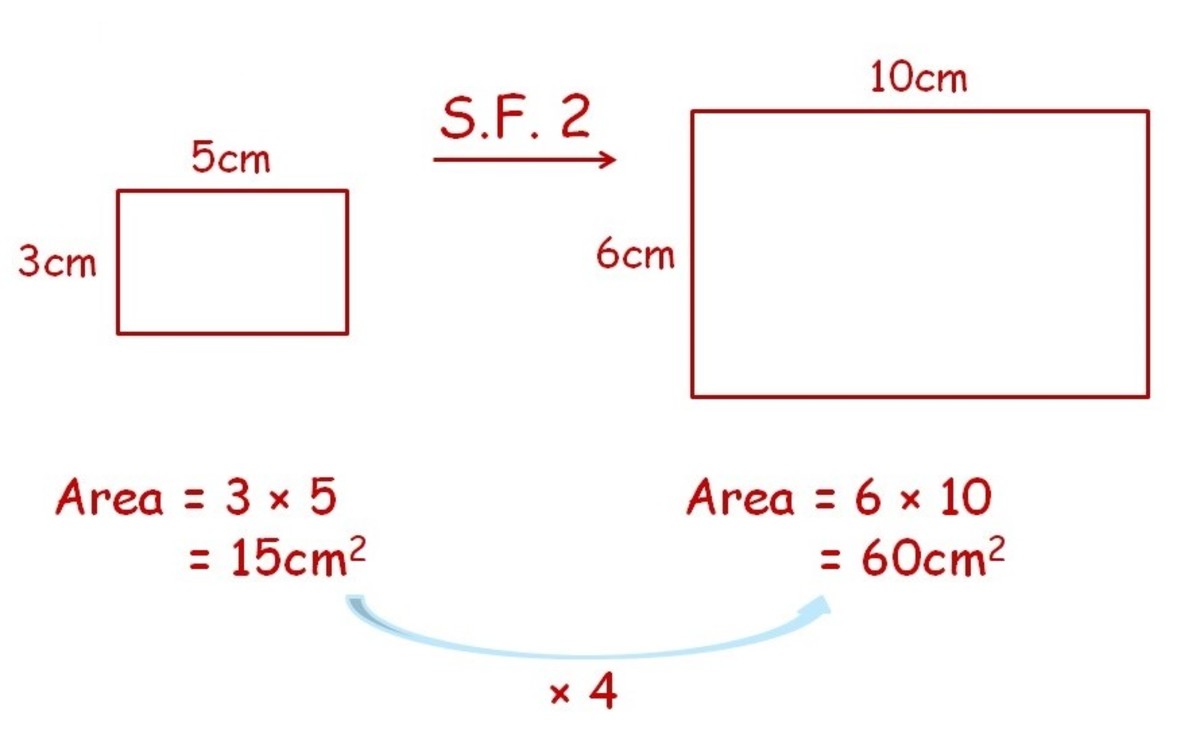
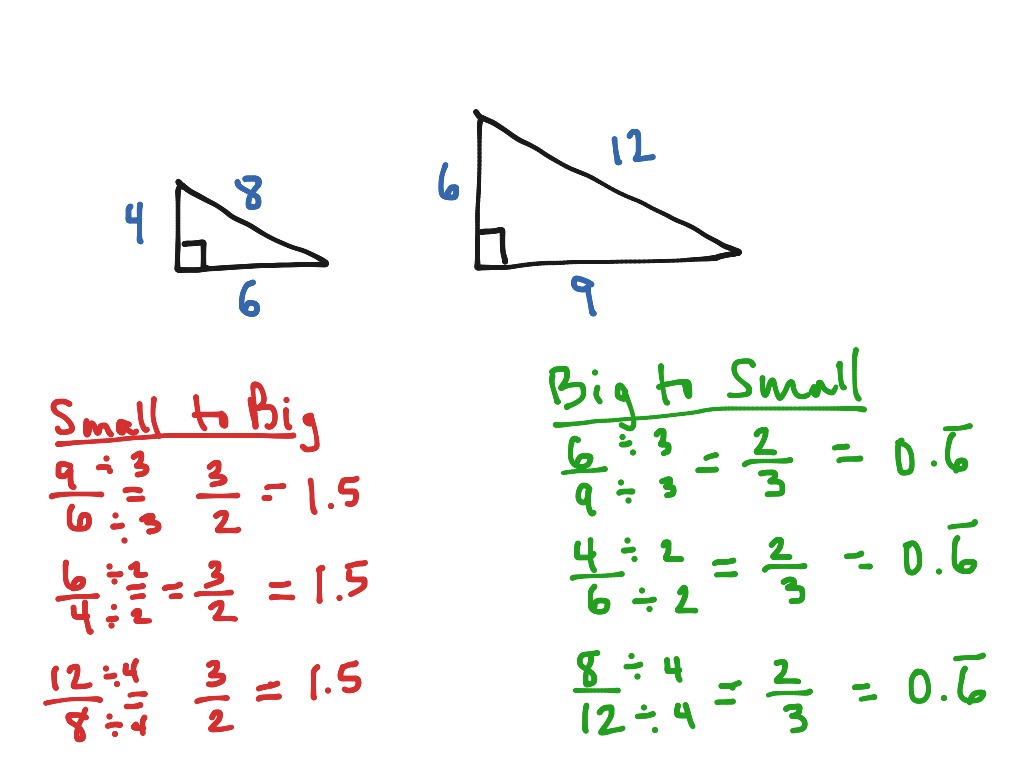
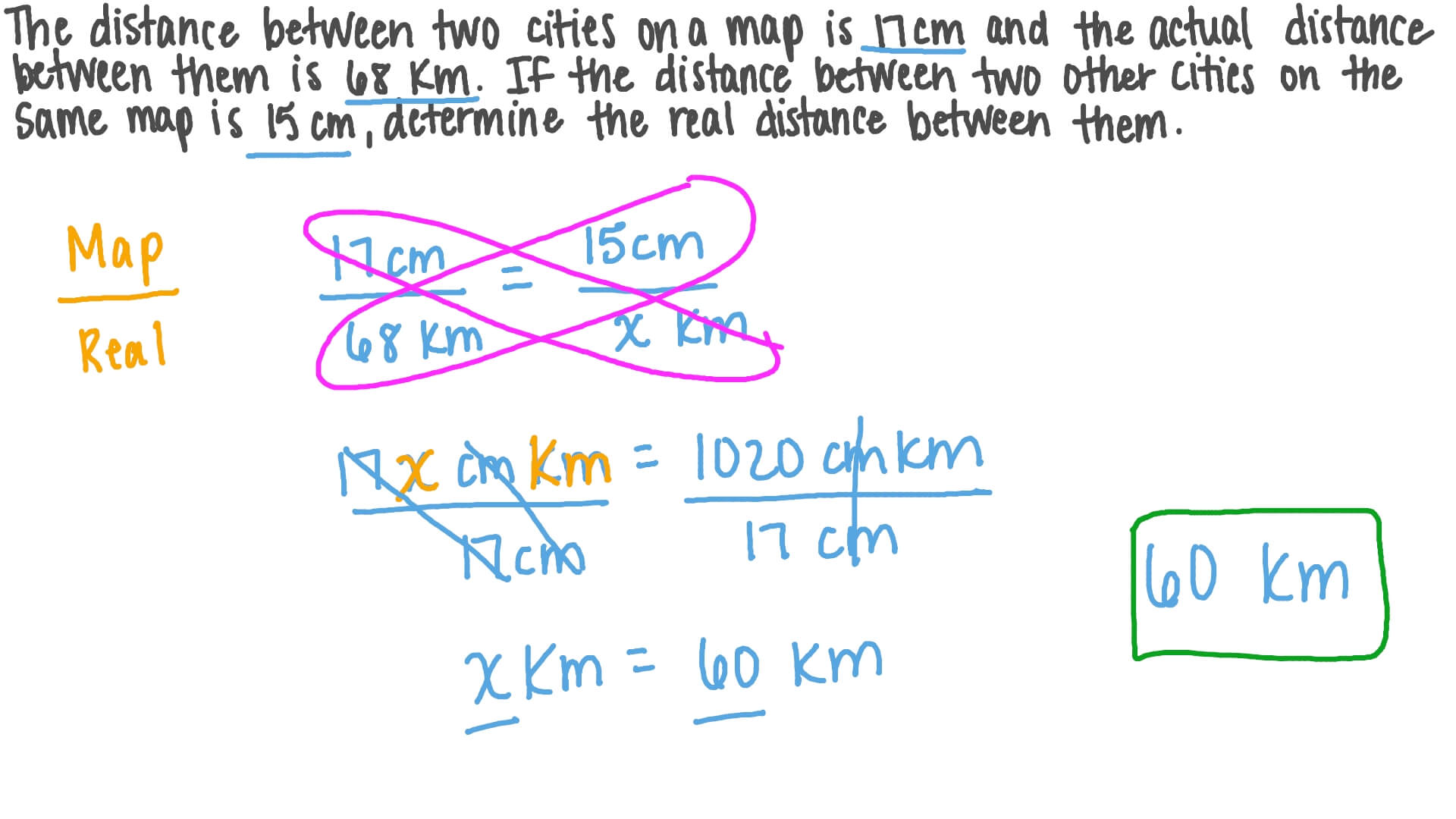
What is the formula to scale a line. In geometry, the ratio of the corresponding sides of two similar figures is called the scale factor. Calculate the size of a missing length, area or volume on a similar figure using the enlargement/reduction scale factor as part of national 5 maths. So let's, just for fun, let's imagine that we pick a point that sits on line a as our center of.
Scale factor = ½ =1:2 (simplified). I'd really like to avoid having the equation number on the next line. Asked 10 years, 8 months ago.
For businesses, understanding the depth and breadth of this logistical enterprise can provide. How do you achieve this? Think of it as first scaling the number down to zero (of the domain set), then multiply with the multiplying factor and then scaling it back up from zero (of the range set).
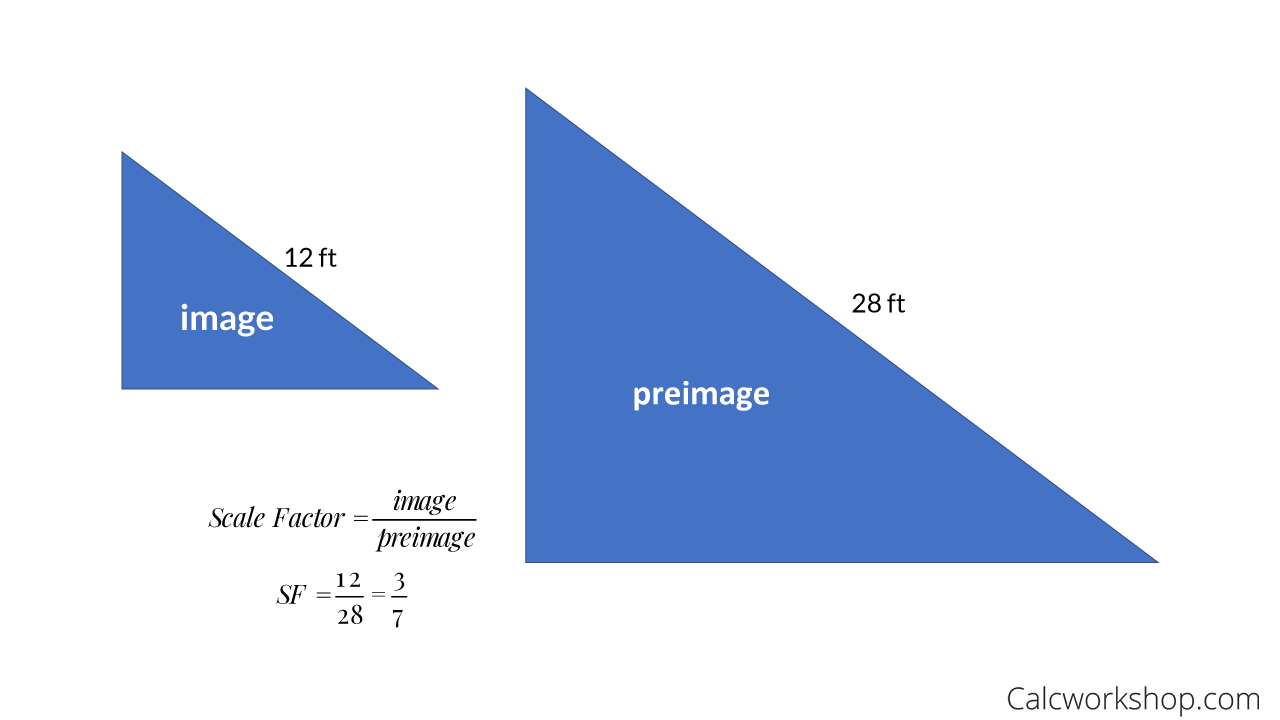
Modified 10 years, 8 months ago. 6 x scale factor = 3. To find scale factor, start by finding the length of a corresponding side on each figure.
Since the scale factor is a ratio, the first step to finding it is to use the following formula: These operations are called scaling. (1, 20) is on the line (100, 80) is one the line slope is:
A dilation is a type of transformation that changes the size of the image. F′(sx) = f(x), f ′ ( s x) = f ( x), where s s is the scaling factor. You need to be more specific about what you're looking for.
Hence, the scale factor from the larger square to the smaller square is 1:2. The diagram at the right shows , center. What happens if we dilate an entire line, but the center of the dilation in not on the line?
A graph scale, or simply scale, refers to a set of numbers that indicate certain intervals on a graph used for measurement. Scale factor = scaled size / real size. Define a dilation that maps line a onto line b by choosing a center and a scale factor.
How do you find the scale. What is a scale factor? How to scale a function?
In affine geometry, uniform scaling (or isotropic scaling [1]) is a linear transformation that enlarges (increases) or shrinks (diminishes) objects by a scale factor that is the same in all directions. A dilation takes a line not passing through the center of the dilation to a parallel line. The rules you given do not produce a consistent linear scaling.