Outrageous Tips About Acceleration From Position Time Graph Multiple Y Axis
Change in velocity is always calculated as the final velocity, v.
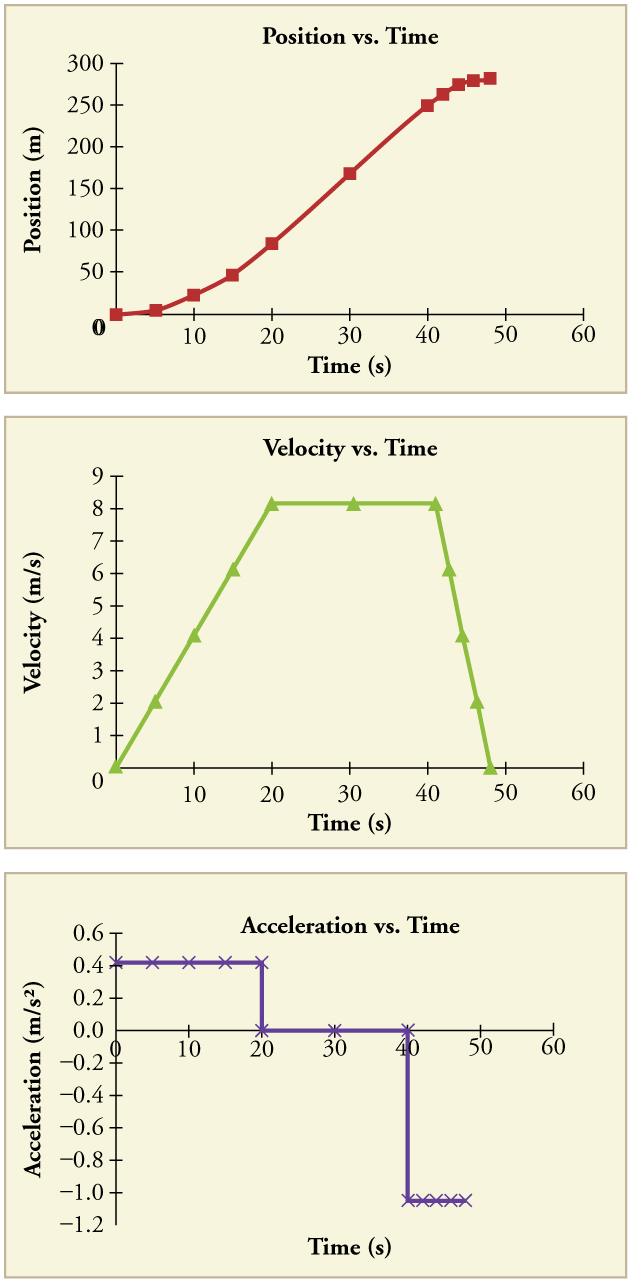
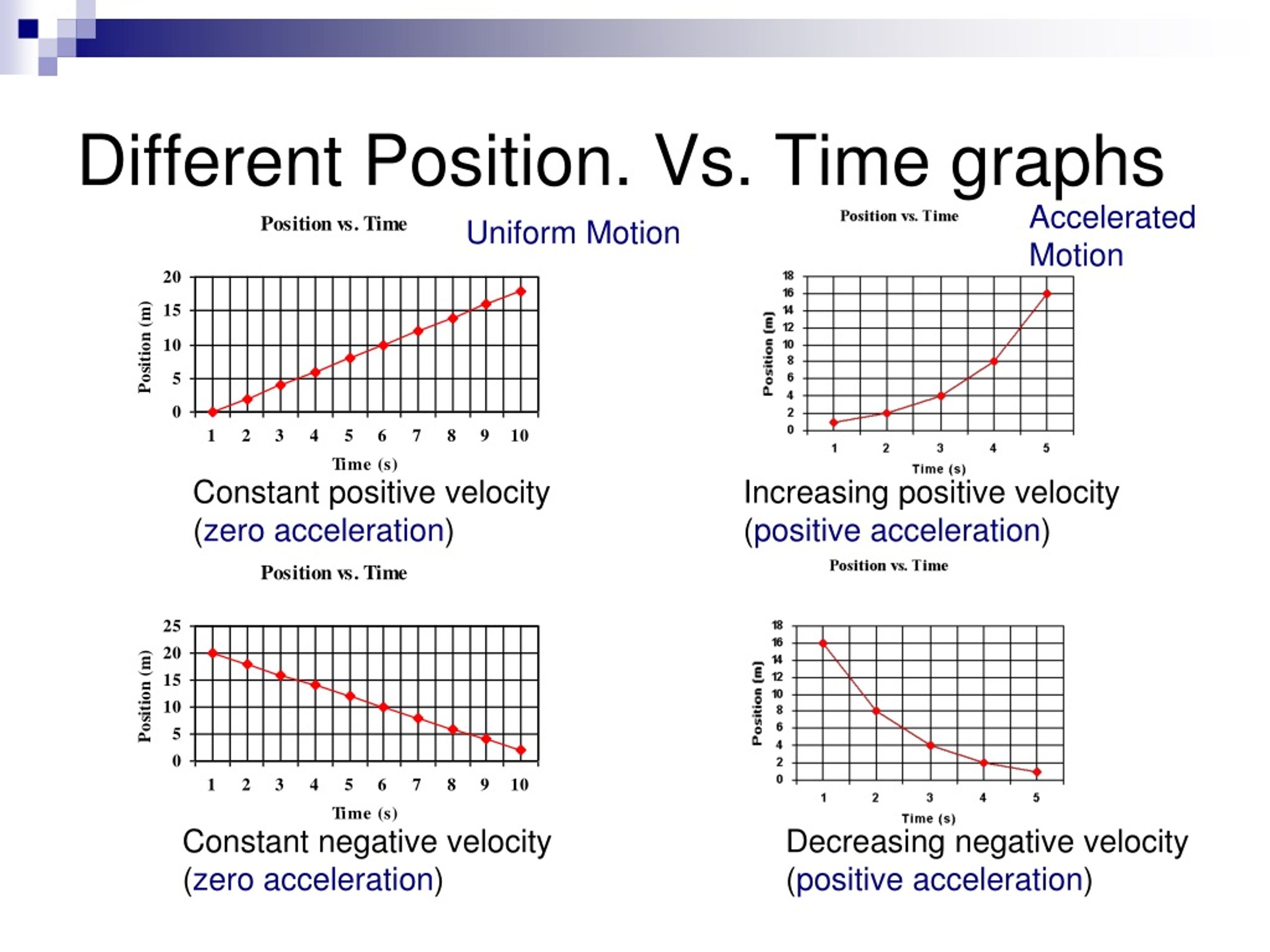
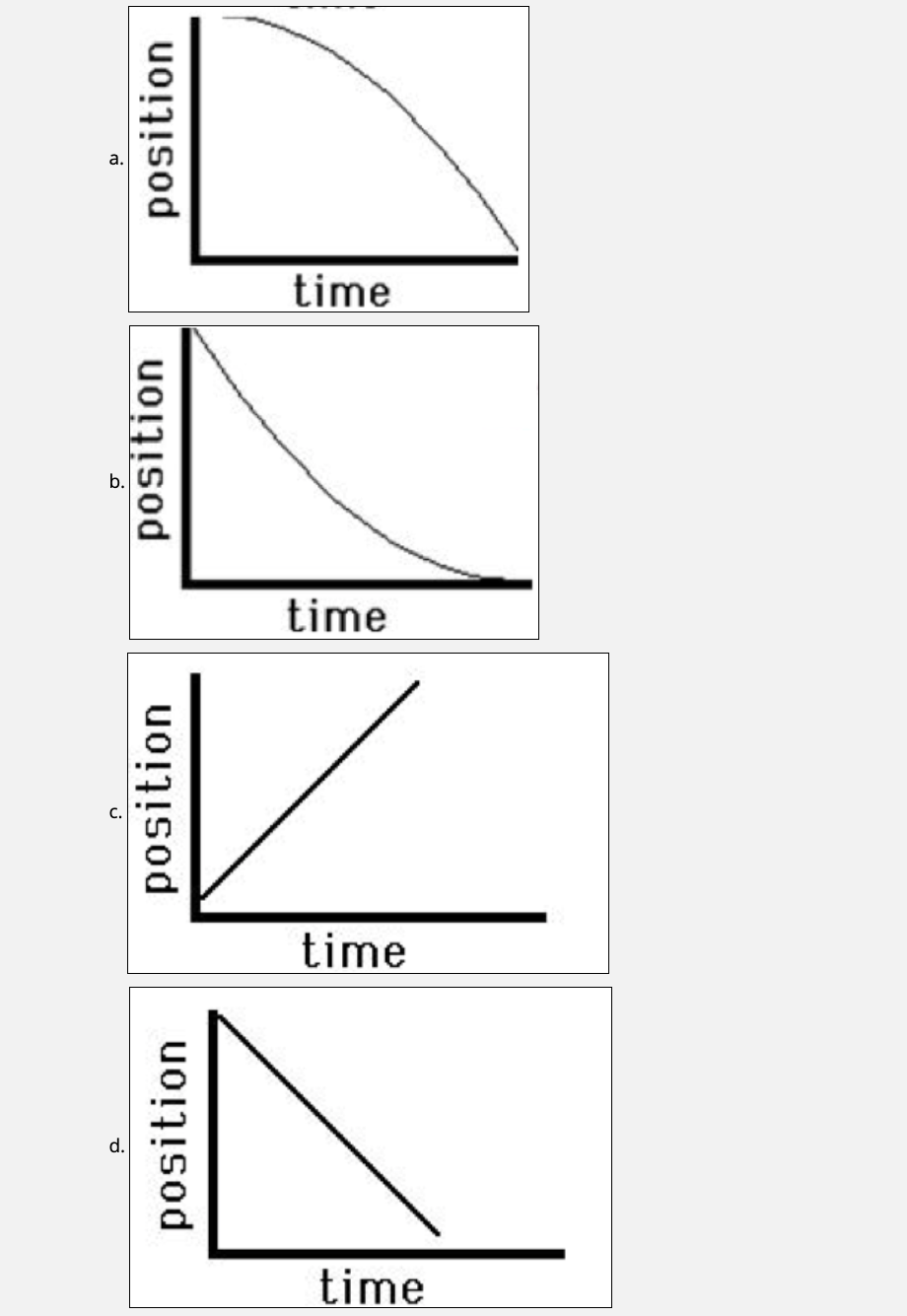
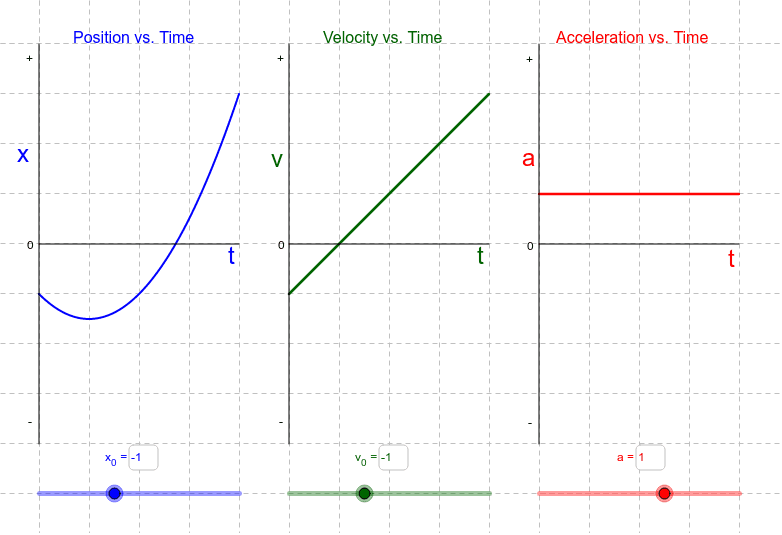
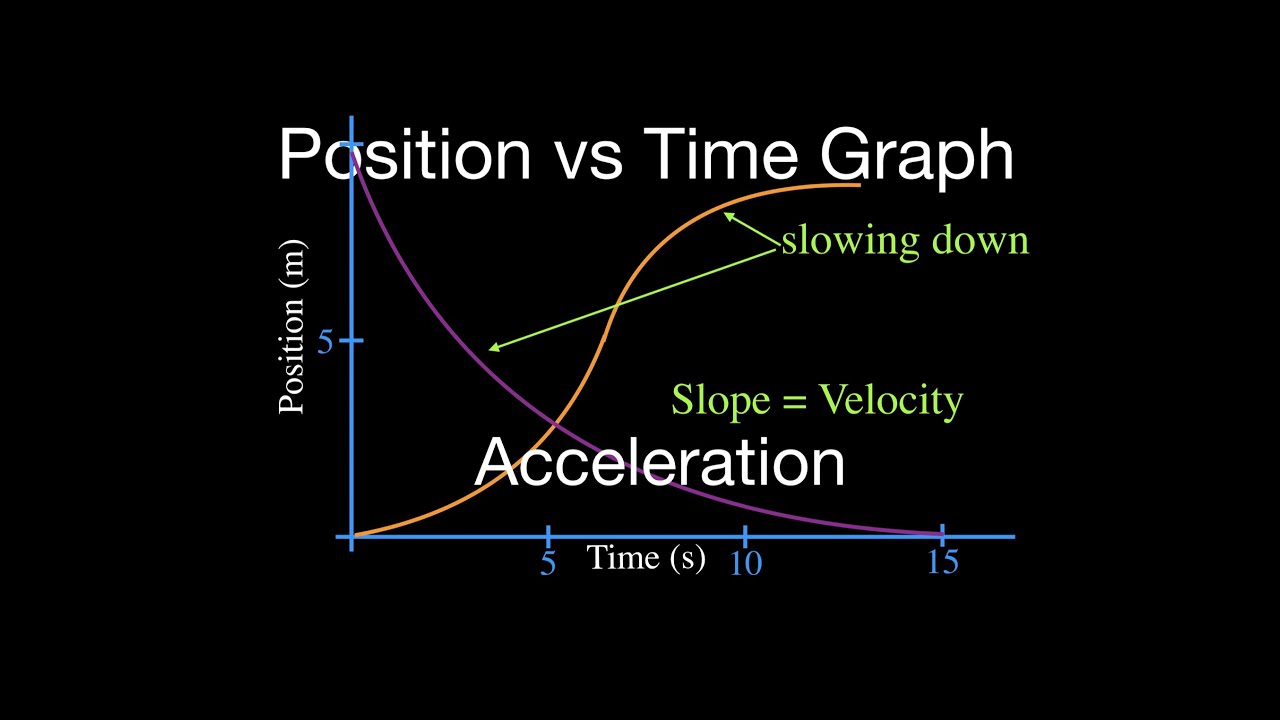
Acceleration from position time graph. Explanation of position time graph for uniformly accelerated motion for uniformly accelerated motion along a straight line the position time relation will be given as, x = x. Section key terms acceleration graphing velocity as a function of time earlier, we examined graph s of position versus time. These are acceleration vs time graphs.
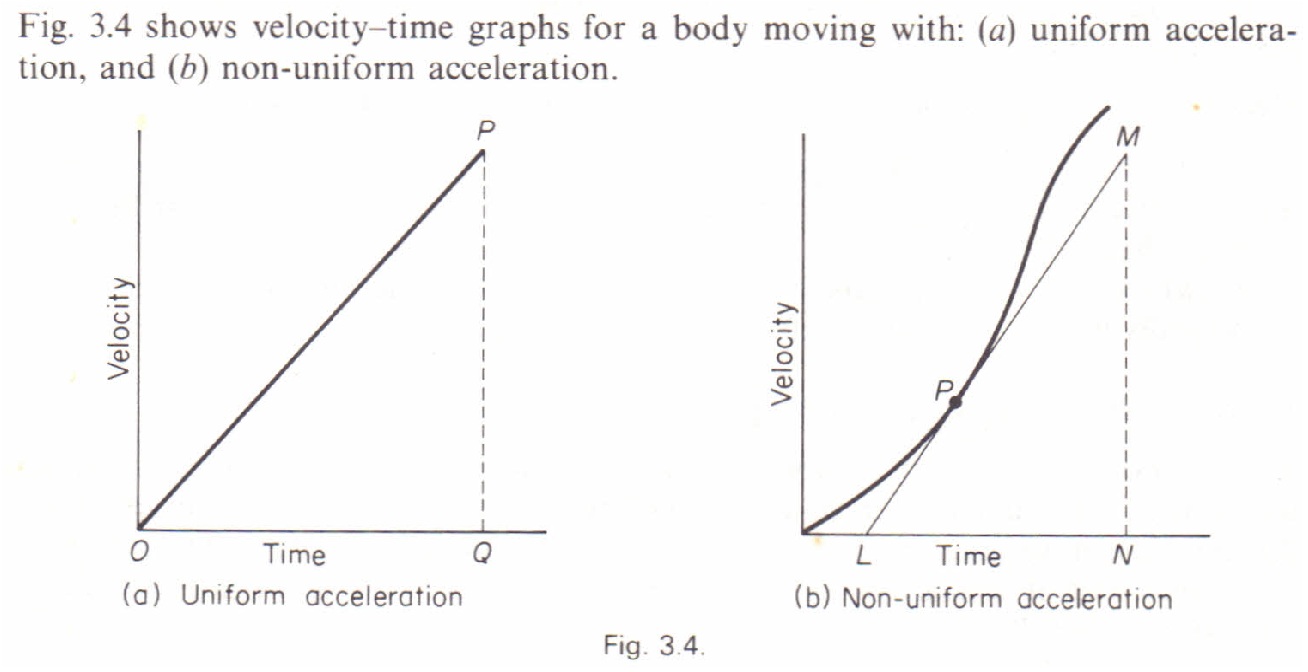
And a line below the time axis indicates negative acceleration. Pay attention to the shape of the graph. Now, we are going to build on that.
Using the graph to determine displacement, distance, average velocity, average speed, instantaneous velocity, and instantaneous. The connection between position, time, and acceleration. Remember that acceleration is a vector.
Next, use the kinematics equation δx=12at2+v0t\delta x=\frac 12 at^2+v_0tδx=21at2+v0t. These motions can only be related by the time. How do we calculate acceleration in general.
How to read a position vs. .more this physics video tutorial provides a basic introduction into motion graphs such as position time graphs, velocity time graphs, and acceleration time. Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity with time.
An object’s horizontal position, velocity, or acceleration does not affect its vertical position, velocity, or acceleration. Send feedback | visit wolfram|alpha. Having the initial velocity v0v_0v0, calculate the displacement δx\delta xδx between two known points on the graph.
The slope and curvature of the graph provide important information about the. We define acceleration, a, as the change in velocity divided by time. Acceleration is a vector that points in the same direction as the change in velocity, though it may not always be in the direction of motion.
3.4 the initial displacement d 0 is often 0, in which case the equation can be written as v ¯ = d t this equation, which is the definition of average velocity and valid for both constant. Time graph for an object whose acceleration changes with time. Between \(t\) = 2.2 s and \(t\) = 2.5 s, as the object.

![Thread by Doc_MD18 "NMAT Review Must Know Physics [Thread] (Topics](https://pbs.twimg.com/media/DyztVr6VAAAcTJE.jpg)