Painstaking Lessons Of Tips About What Is A Dual Axis Chart With An Example Beautiful Line

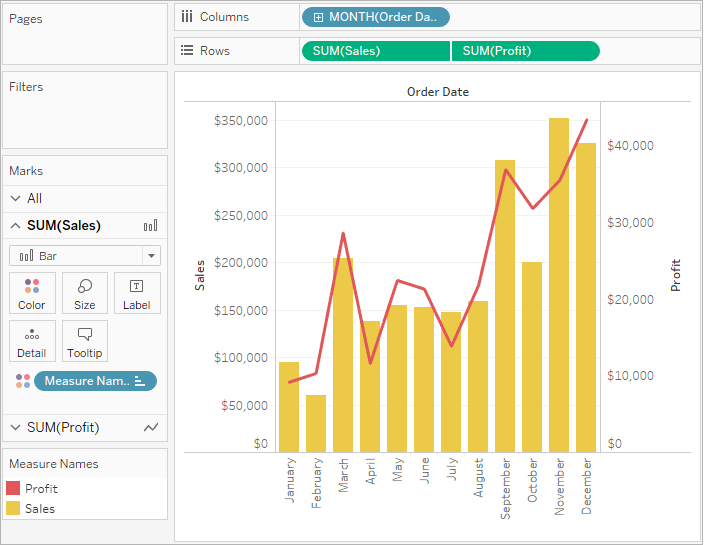
This video introduces the dual axis chart and shows how you can have two mark types on the same chart.
What is a dual axis chart with an example. (1) their traditional use (2) a method for making your end user part of the story and (3) an option for improving the aesthetics of your dashboard. This article explains tableau dual axis charts, their pros, and cons, along with steps you can use to create dual axis charts in tableau. The relationship between two variables is referred to as correlation.
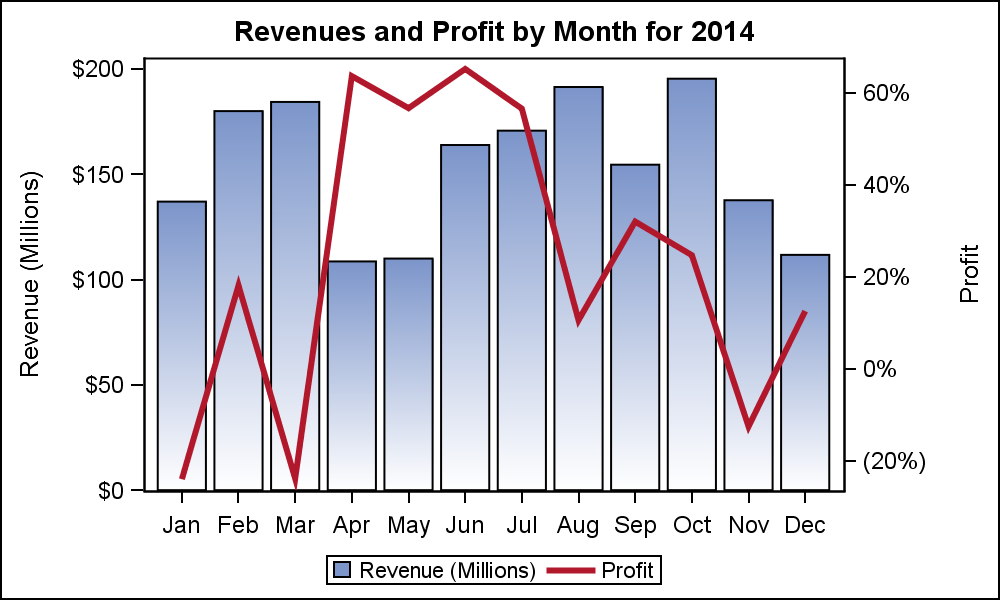
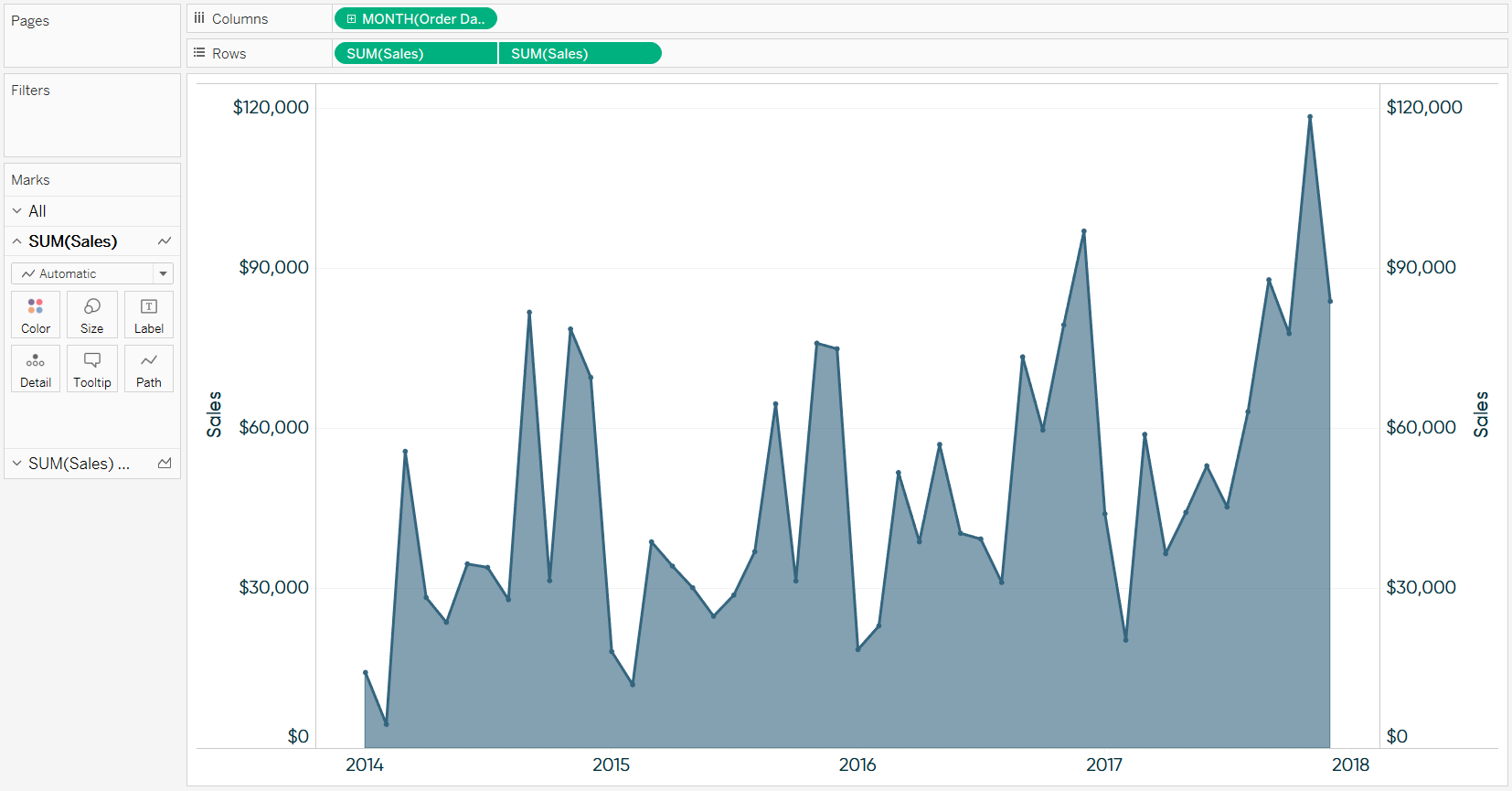
The chart illustrates plenty of information using limited space. A dual axis chart lets you combine measures that differ in scale and units. So, how are they created?
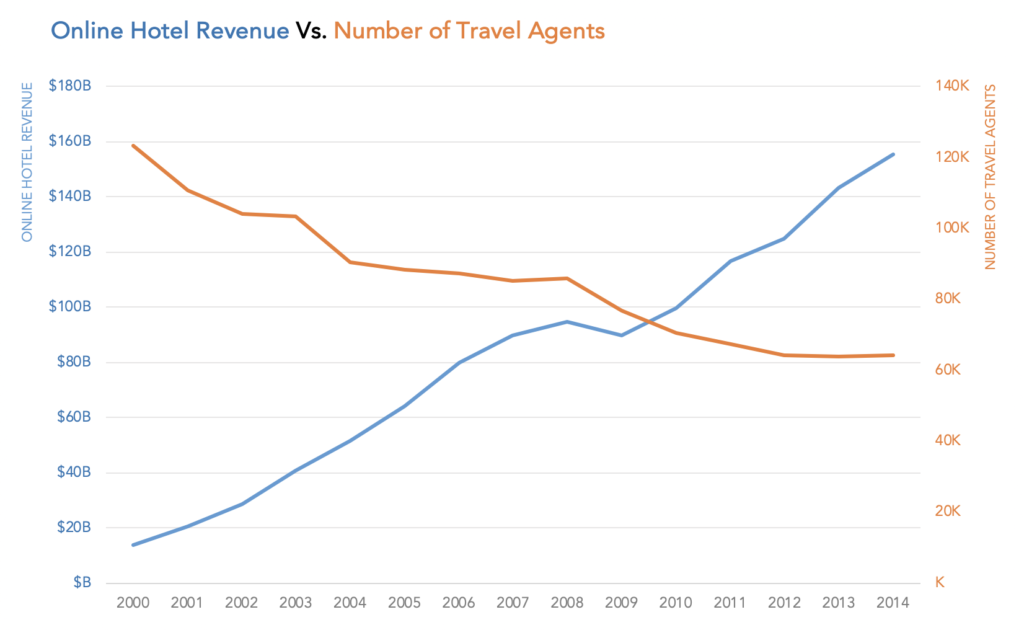
It facilitates comparison between measures with different scales or units. More so, it’s amazingly easy to read and interpret. A dual axis chart also known as multiple axes chart, employs two axes to clearly depict the connections between two variables of varying magnitudes and scales of measurement.
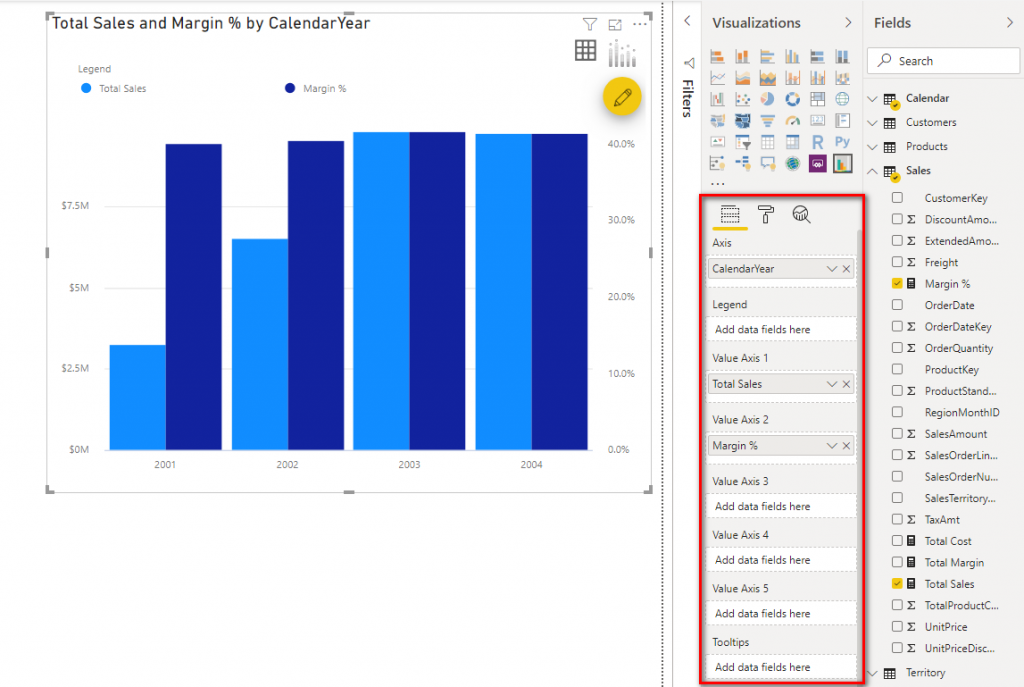
Tableau dual axis charts combine two or more tableau measures and plot relationships between them, for quick data insights and comparison. The dual axis chart allows us to visualize relative trends that might not be immediately obvious when. Correlation is the term used to describe the relationship between two variables.
A dual axis chart uses two axes to illustrate the relationships between two variables easily. This enables you to choose a different mark for each of the measures, letting you create different charts. Dual axis charts, also known as combination (combo) charts, are a type of visualization that combines two different types of charts in a single graph.
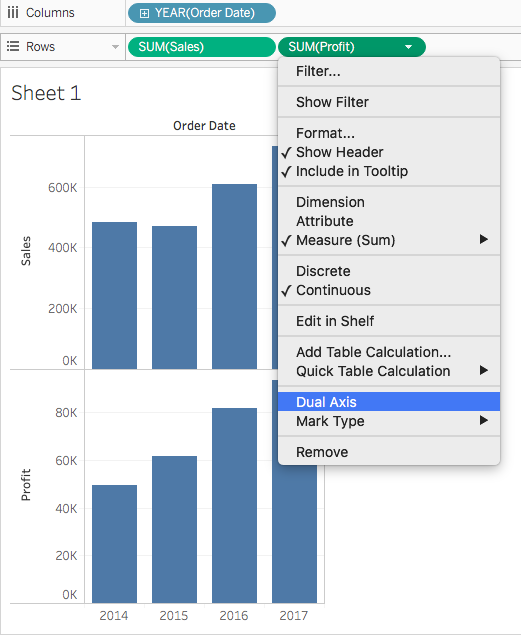
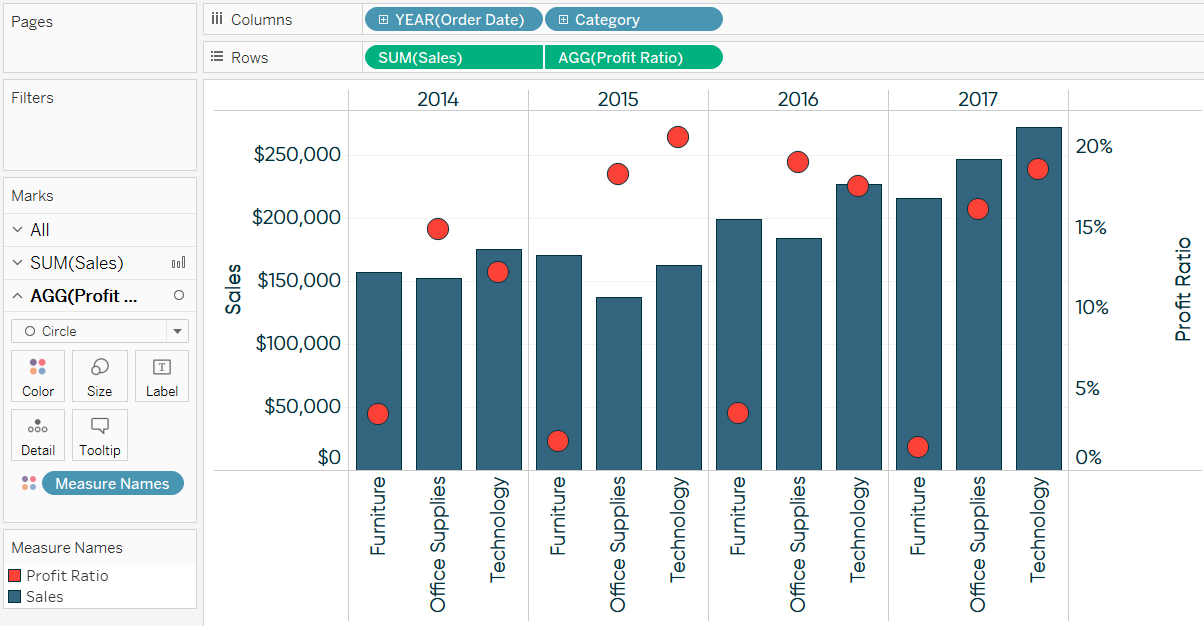
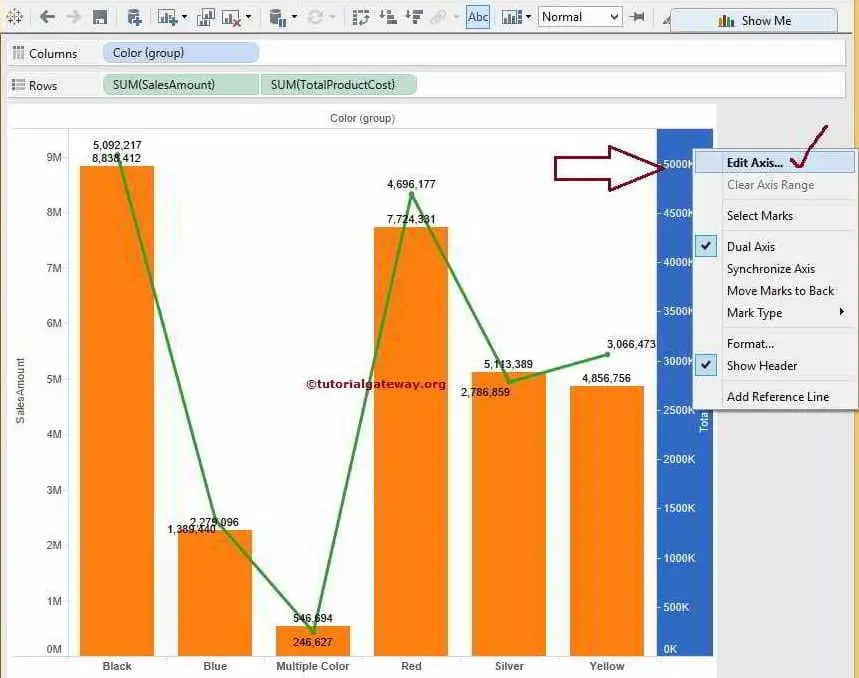
Why do we use dual axis charts? In order to show a line for each gender's change in life expectancy over time on the same set of axes, you'll need to make a dual axis chart. A dual axis chart creates two independent axes (which you can synchronise) that you can plot two separate measures on in the same chart.
The purpose of this type of visualization is to show how one set of data changes concerning another. Learn how to create custom charts, blend measures, and even extend the. We use dual axis charts to compare two trends with each other.
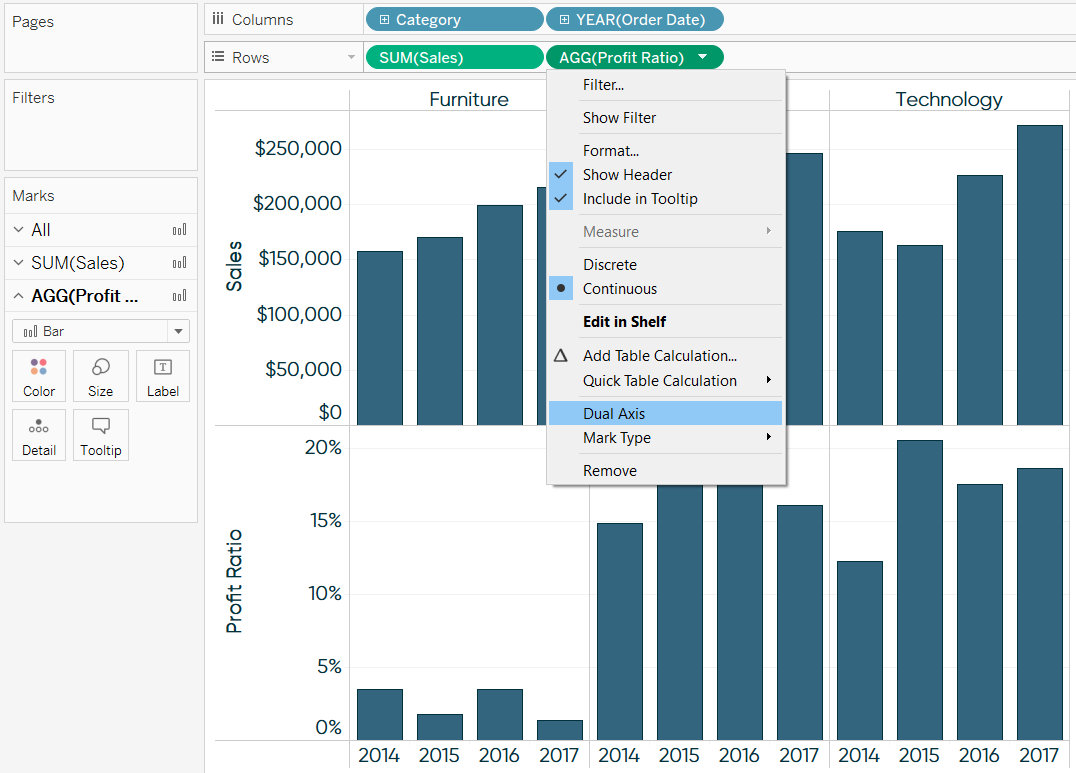
This has one big positive that it creates two separate mark cards for each of the measures. You may be confused and overwhelmed at first. Now the clue is in the title here, dual means we can compare two measures using two different axes.
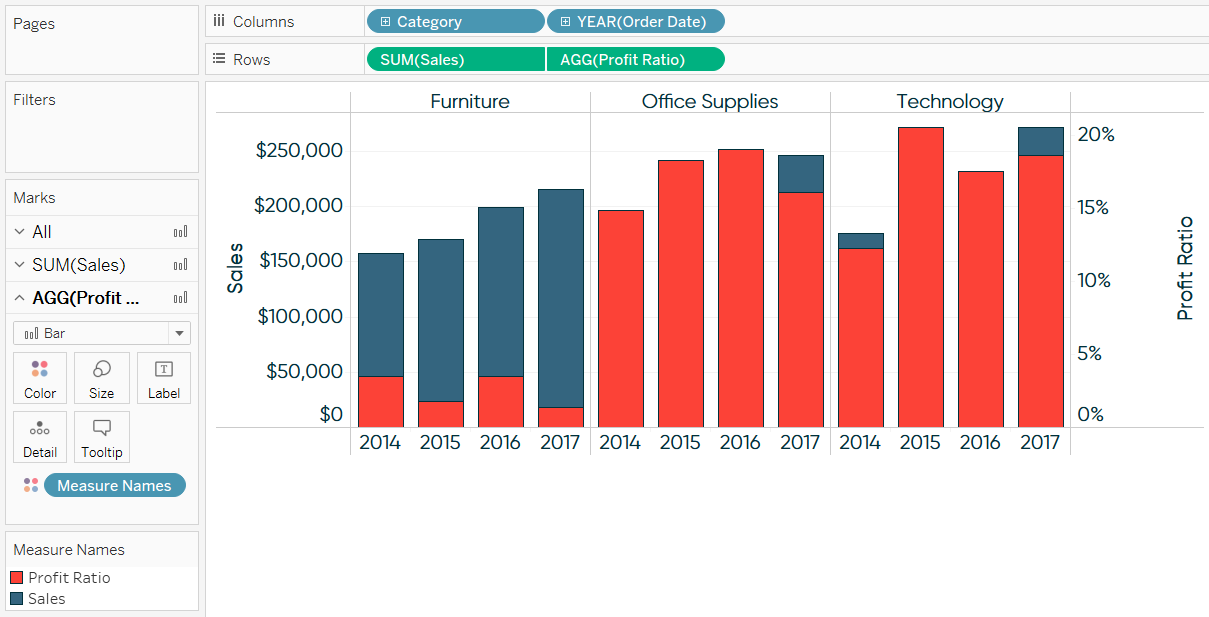
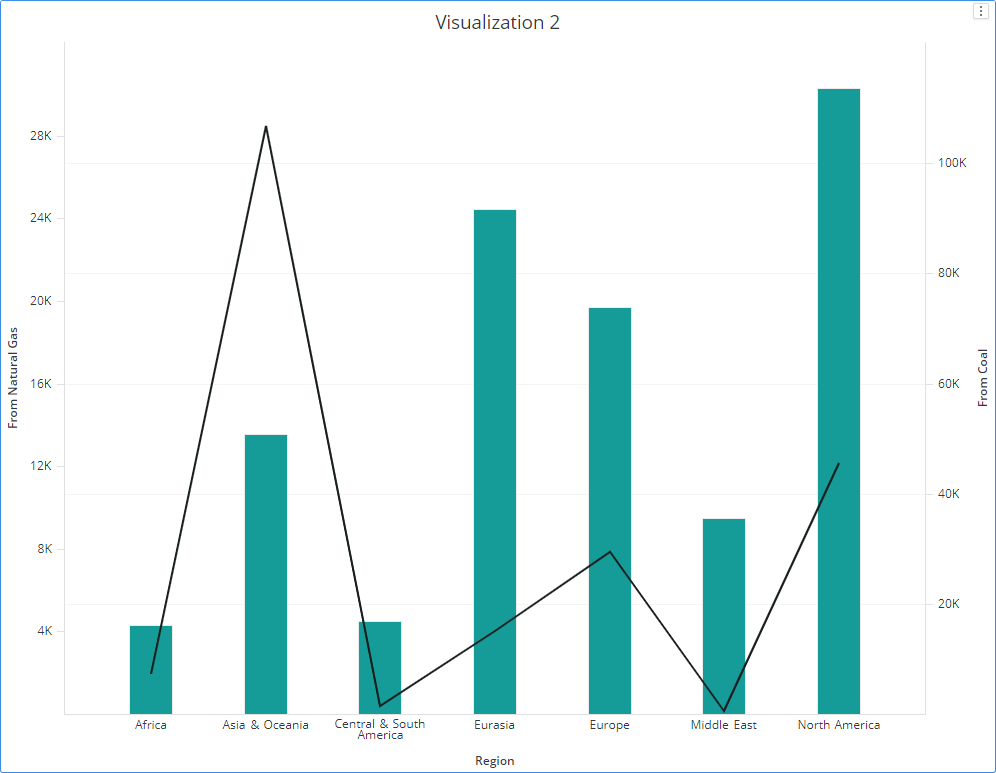
A good use for dual axis charts (possibly the only really good one) is for pareto charts. For example, you can use a dual axis chart to compare revenue and units sold, price and volume, or rainfall and temperature. Why use dual axis charts?
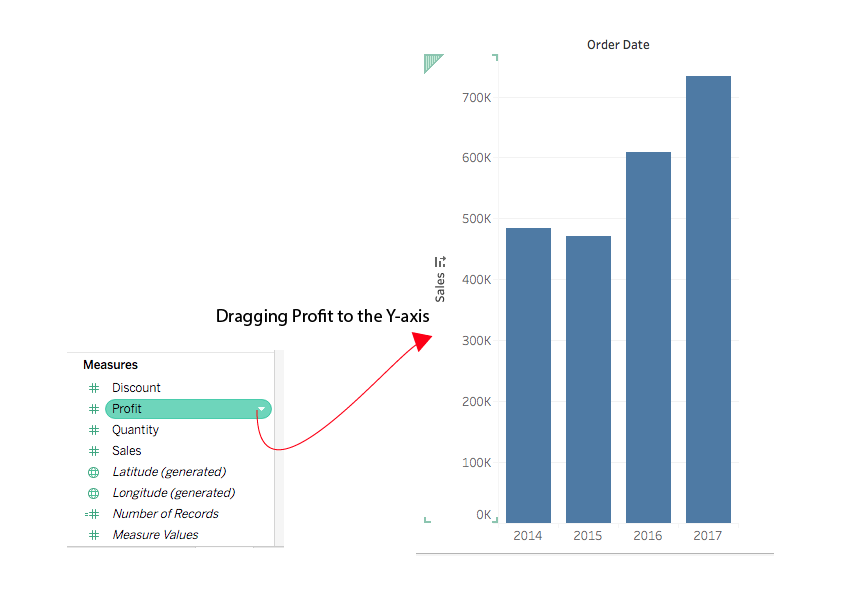
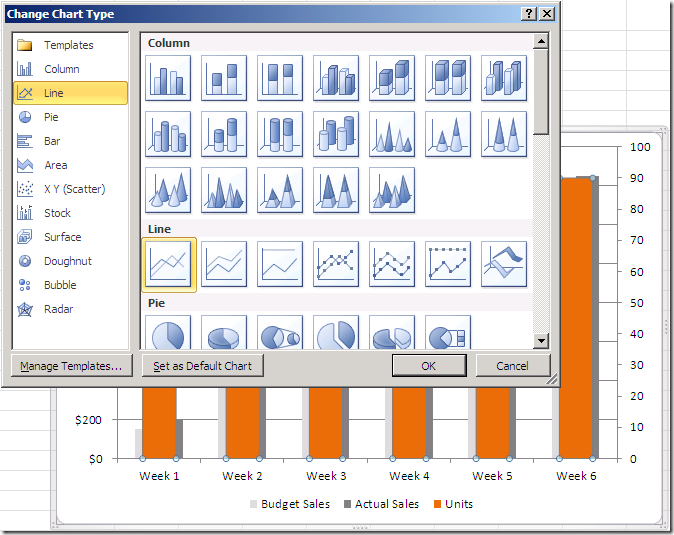
Drag your fields to the rows and columns shelves. A pareto chart combines both the count of an item, and the percentage contribution that count makes to the overall tally. These could be two different data series of the same units but different magnitude or different units altogether.