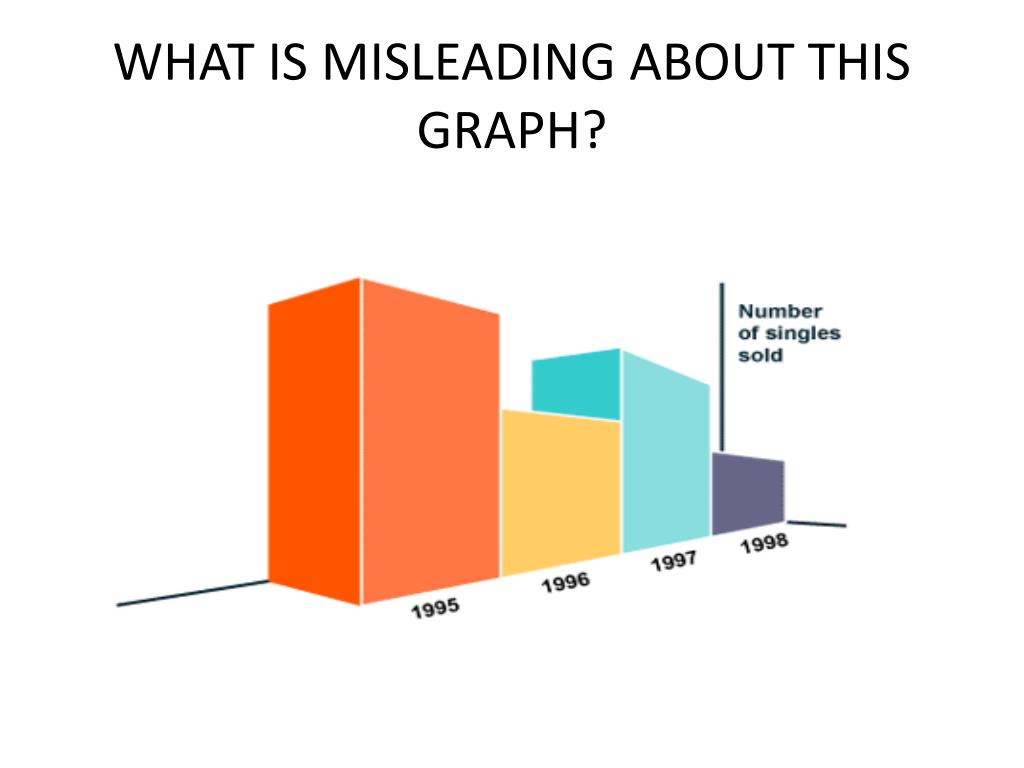
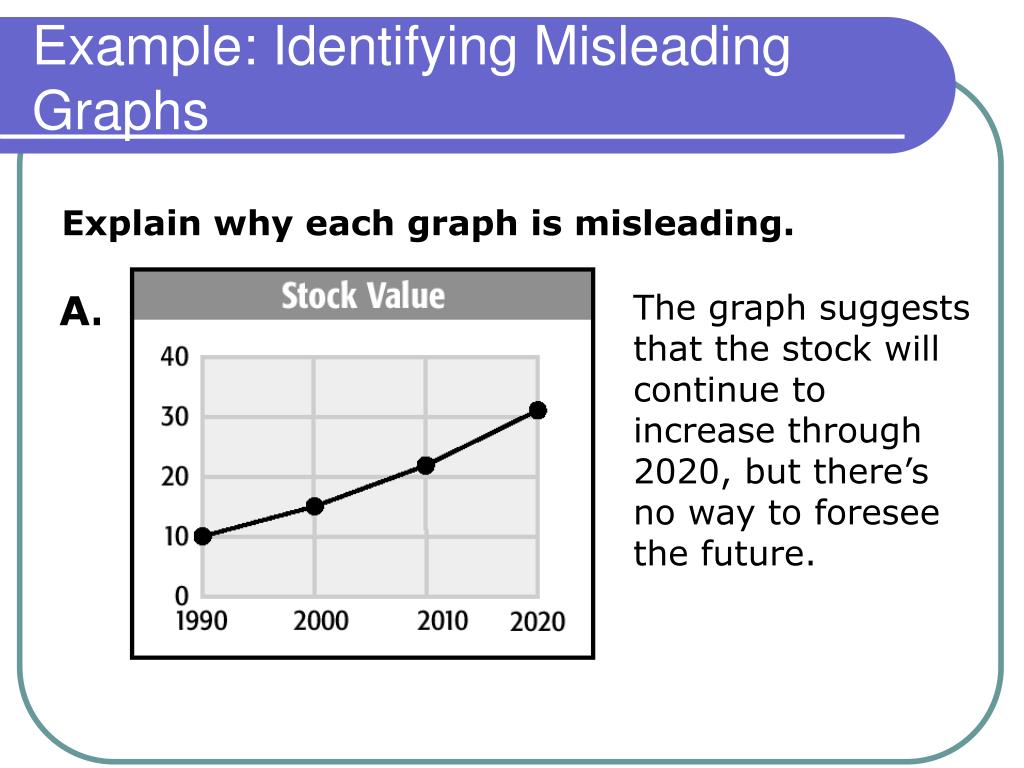
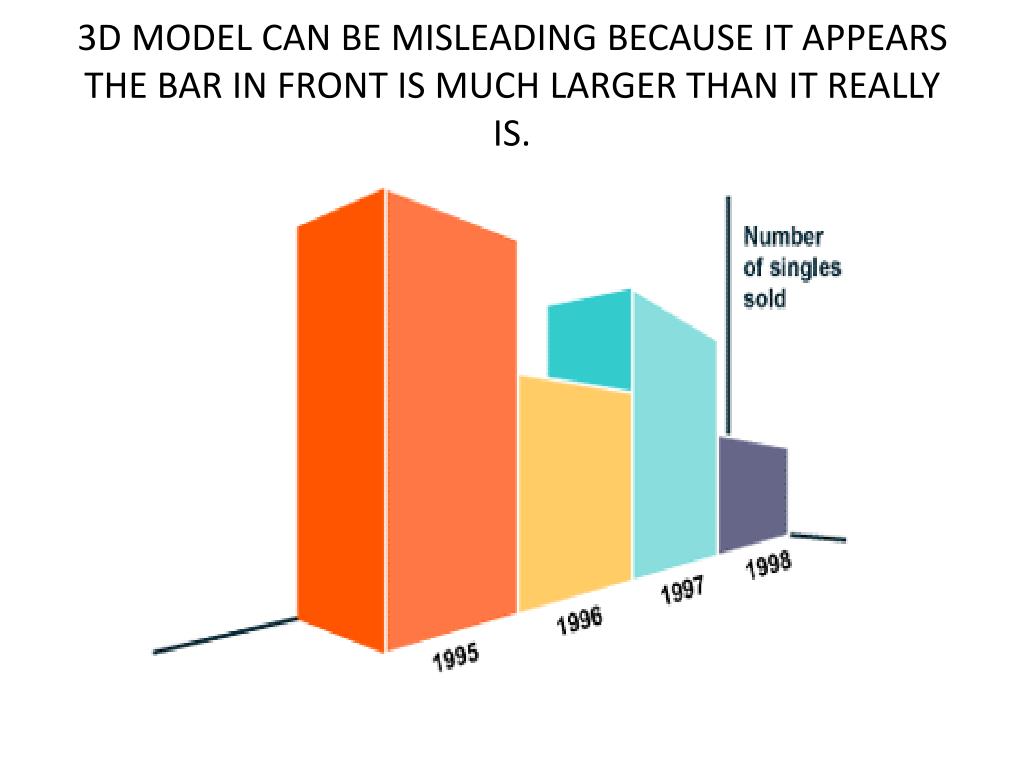
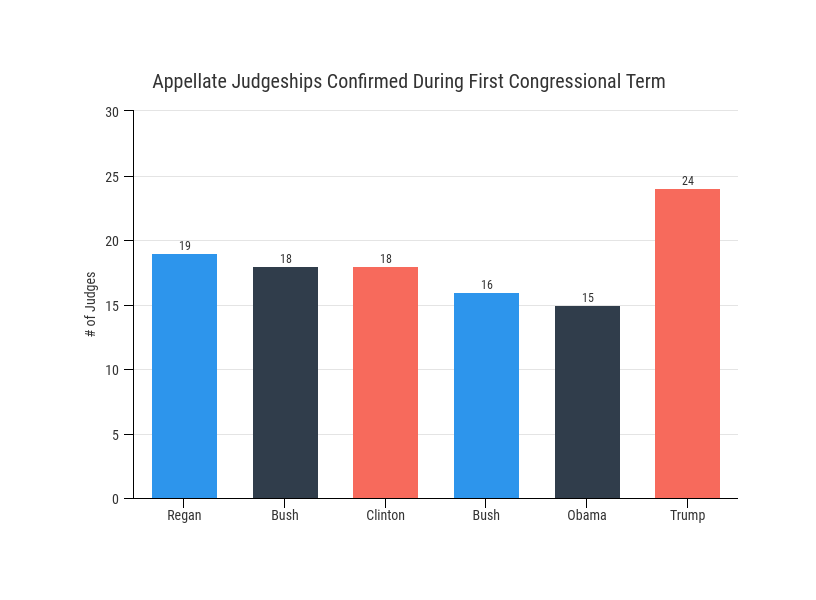
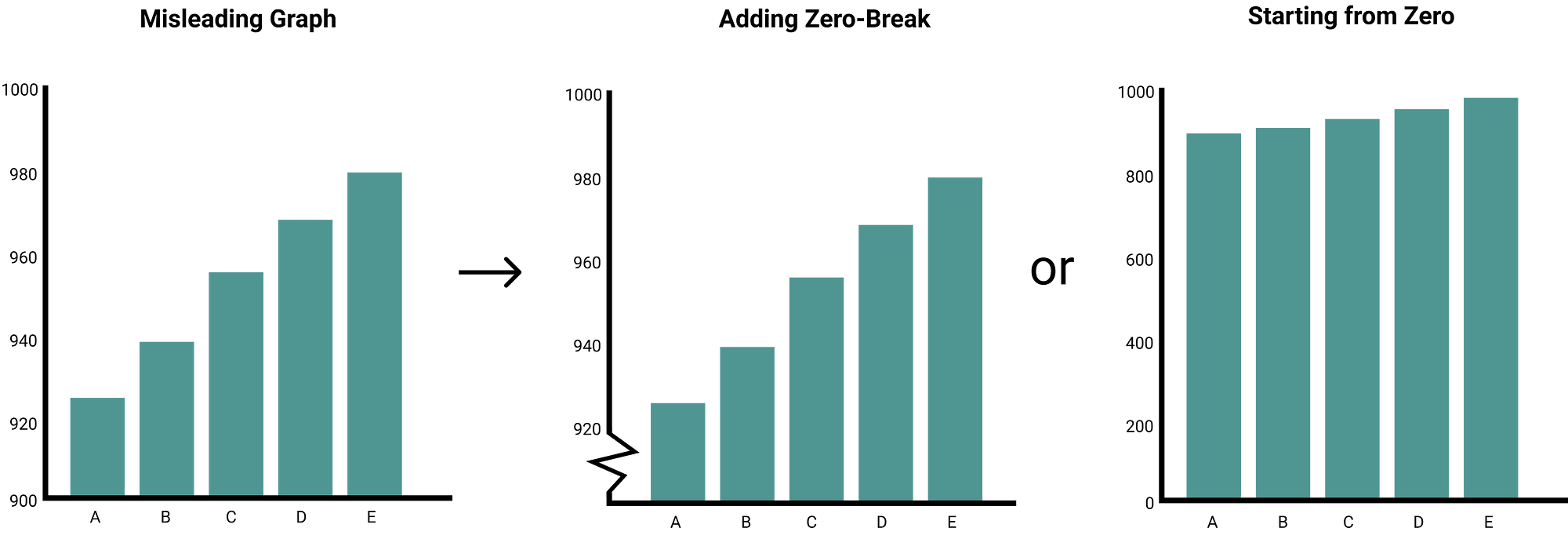Awesome Tips About What Is An Example Of A Misleading Axis Python Plotly Line Chart
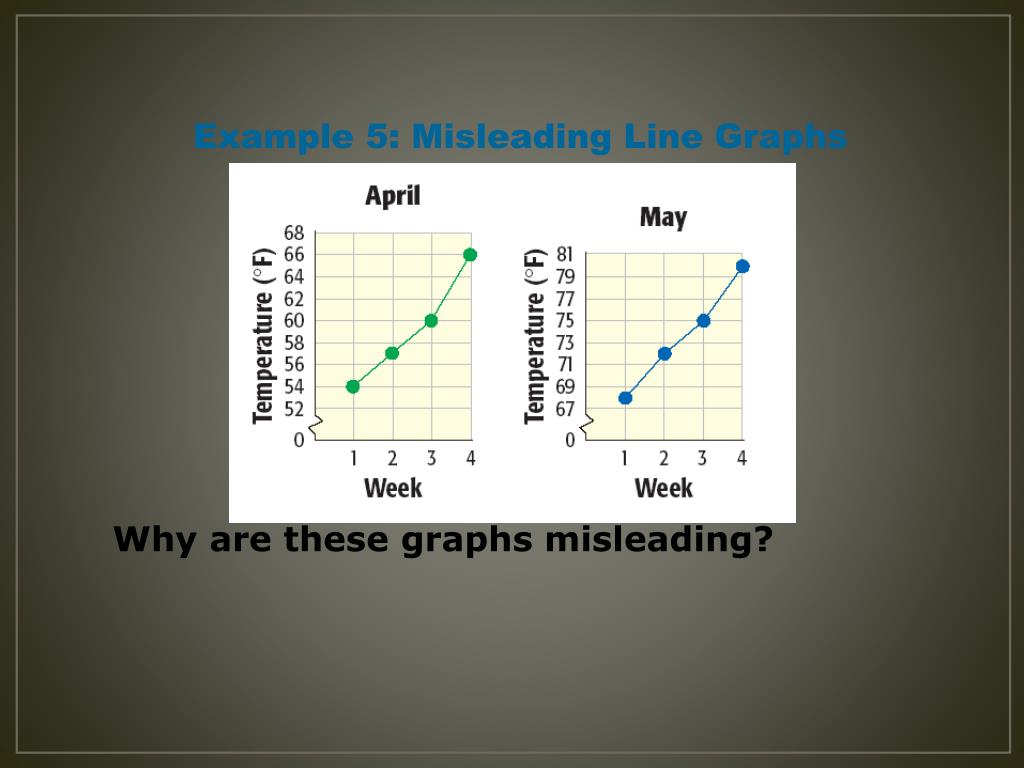
For instance, consider these 2 graphs showing website traffic over the source of a couple months:
What is an example of a misleading axis. The “classic” types of misleading graphs include cases where: Graphs that don’t align with the data. 1) what is a misleading statistic?
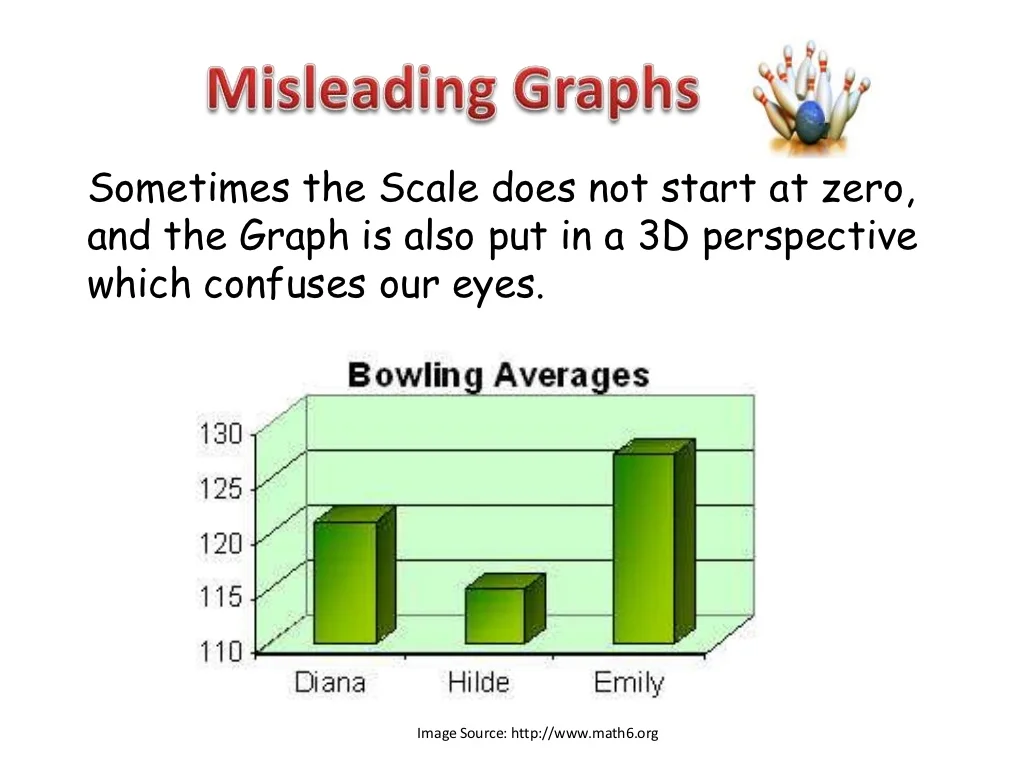
F ( v) = [ m 2 π k t] 3 4 π v 2 e ( − m v 2 2 k t) . The graph starts at 44.5% instead of ‘0’. When talking about scales and axes, one way isn’t necessarily wrong or right, it’s about the message the visualization is designed to convey.
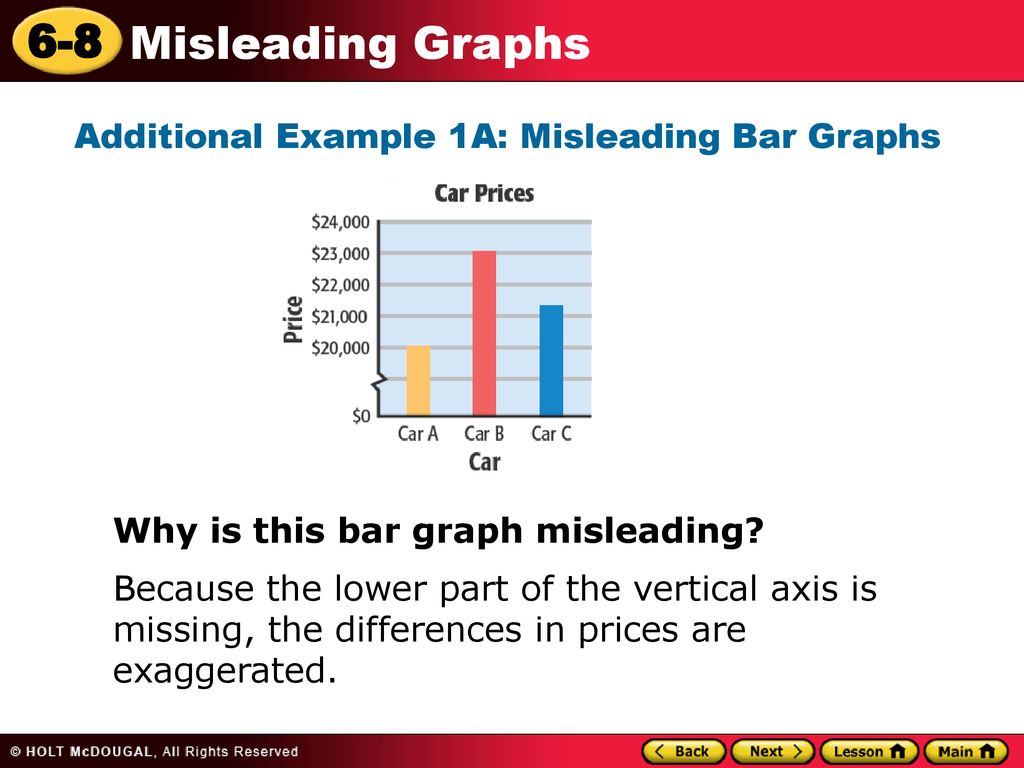
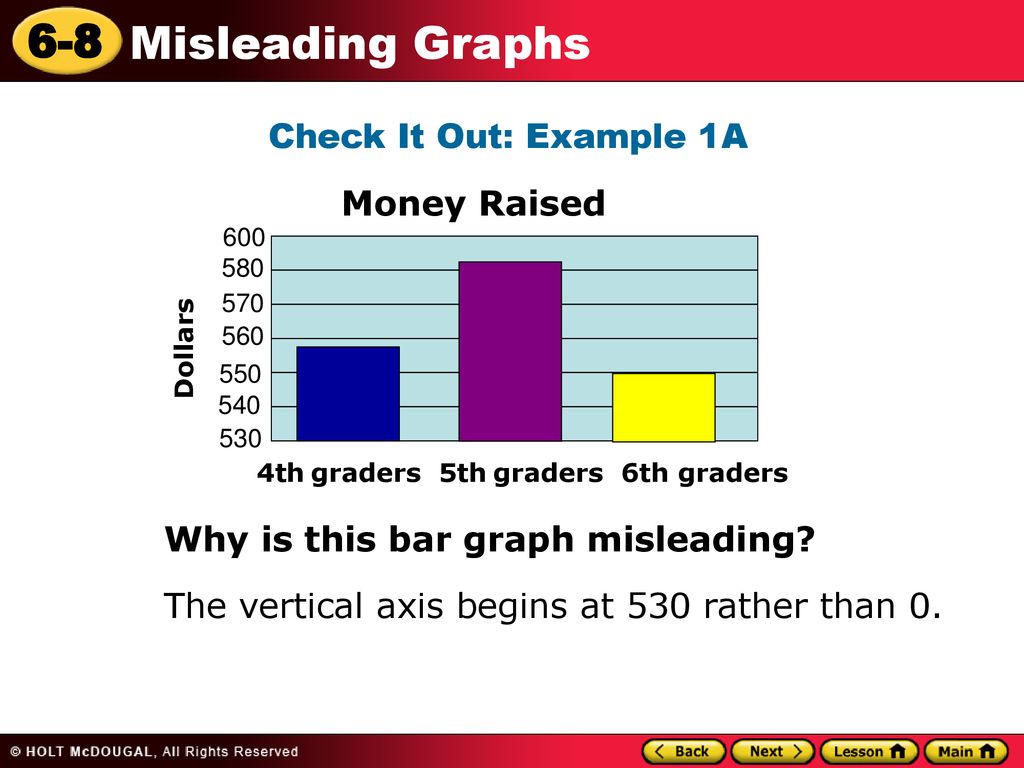
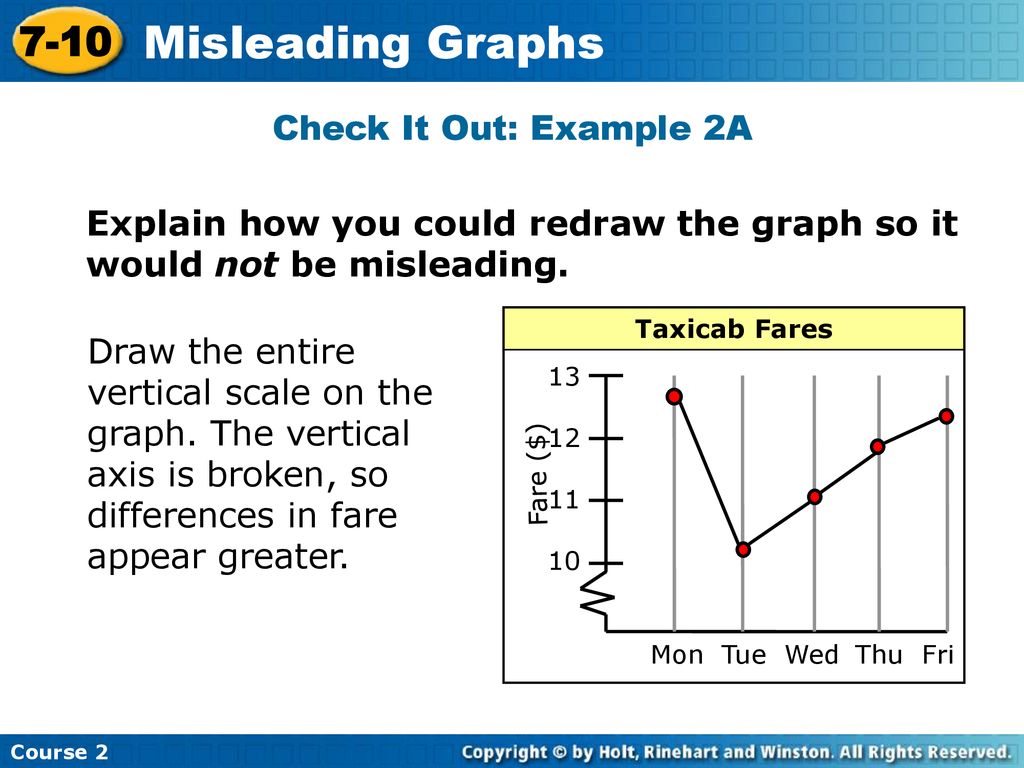
The vertical axis is broken off and does not begin at 0. Graphs may be misleading by being excessively complex or poorly constructed.
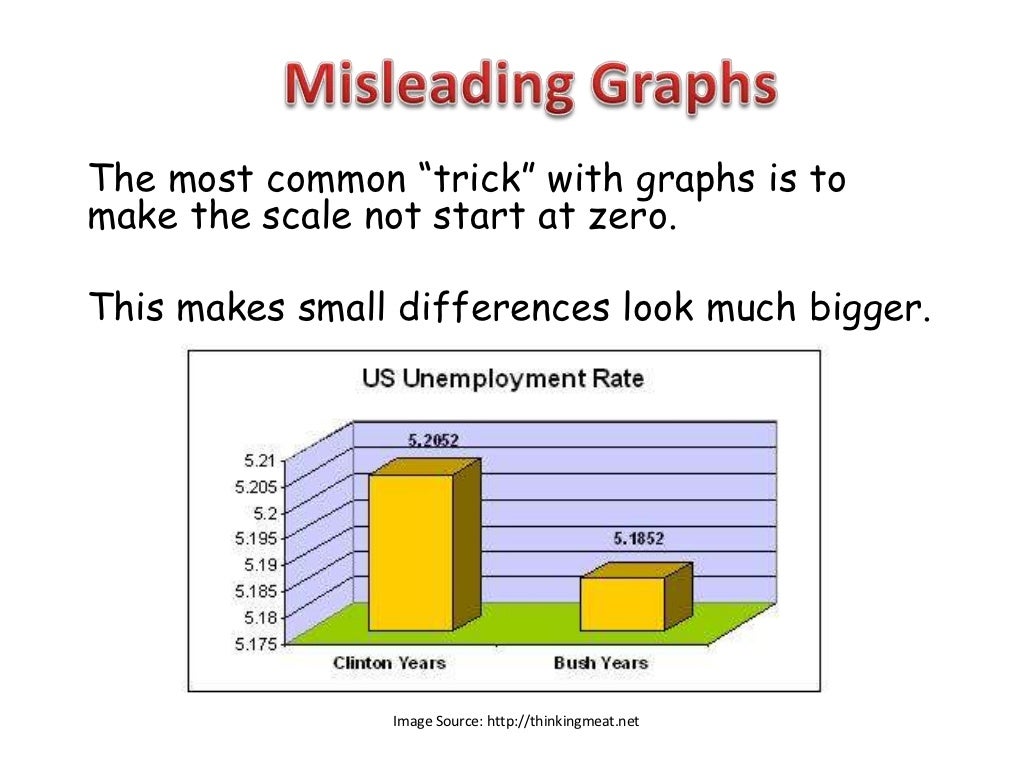
Misleading graph tactic #1: This blows up the differences when comparing data. One of the ways to use charts to manipulate data is to distort scales.
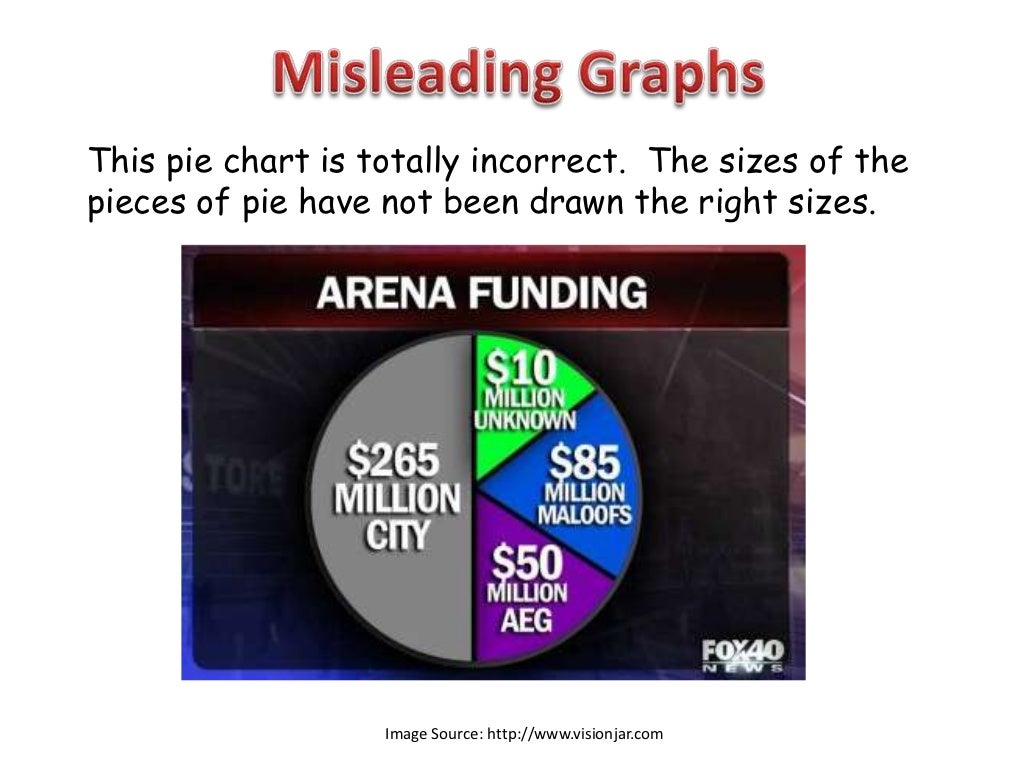
What are the 4 types of bad data visualizations? Pie charts are a popular choice for visualizing data, but they can often lead to misleading data visualization examples. The quantity f ( v) gives the probability density as a function of the speed v .
Graph has a vertical axis starting at the zero baseline and shows there is only a small difference in the proportion in favour of the bill. The “note” section contain 24 examples of misleading graphs. The answer is two characteristics that are misleading are:
Consider a specific example of an entangled state: 4) how can statistics be misleading. 3) misleading statistics examples in real life.
This equation says that the probability density depends on the temperature t of the gas, the mass m of the molecules, and. Good visualization can bring out important aspects of data, but visualization can also be used to conceal or mislead. You may have noticed this graph has a truncated scale (missing baseline)!
In statistics, a misleading graph, also known as a distorted graph, is a graph that misrepresents data, constituting a misuse of statistics and with the result that an incorrect conclusion may be derived from it. Let’s have a look at the graph below to see how a truncated graph might distort data. There are various clues that can lead to questioning the accuracy of a graphical representation.
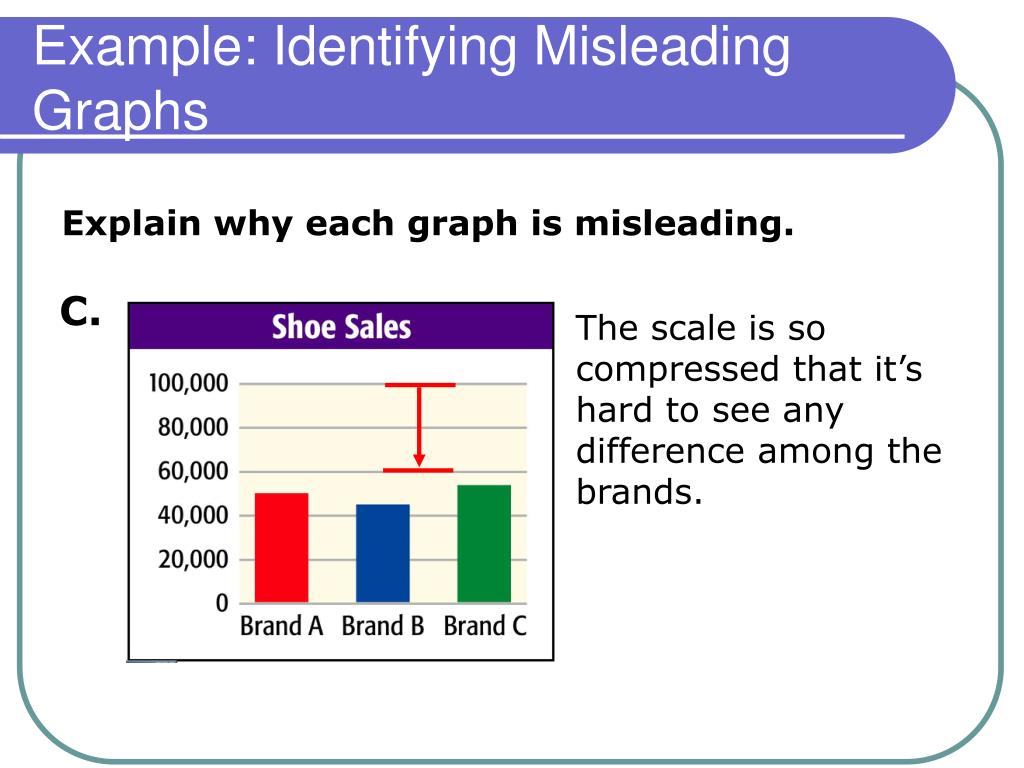
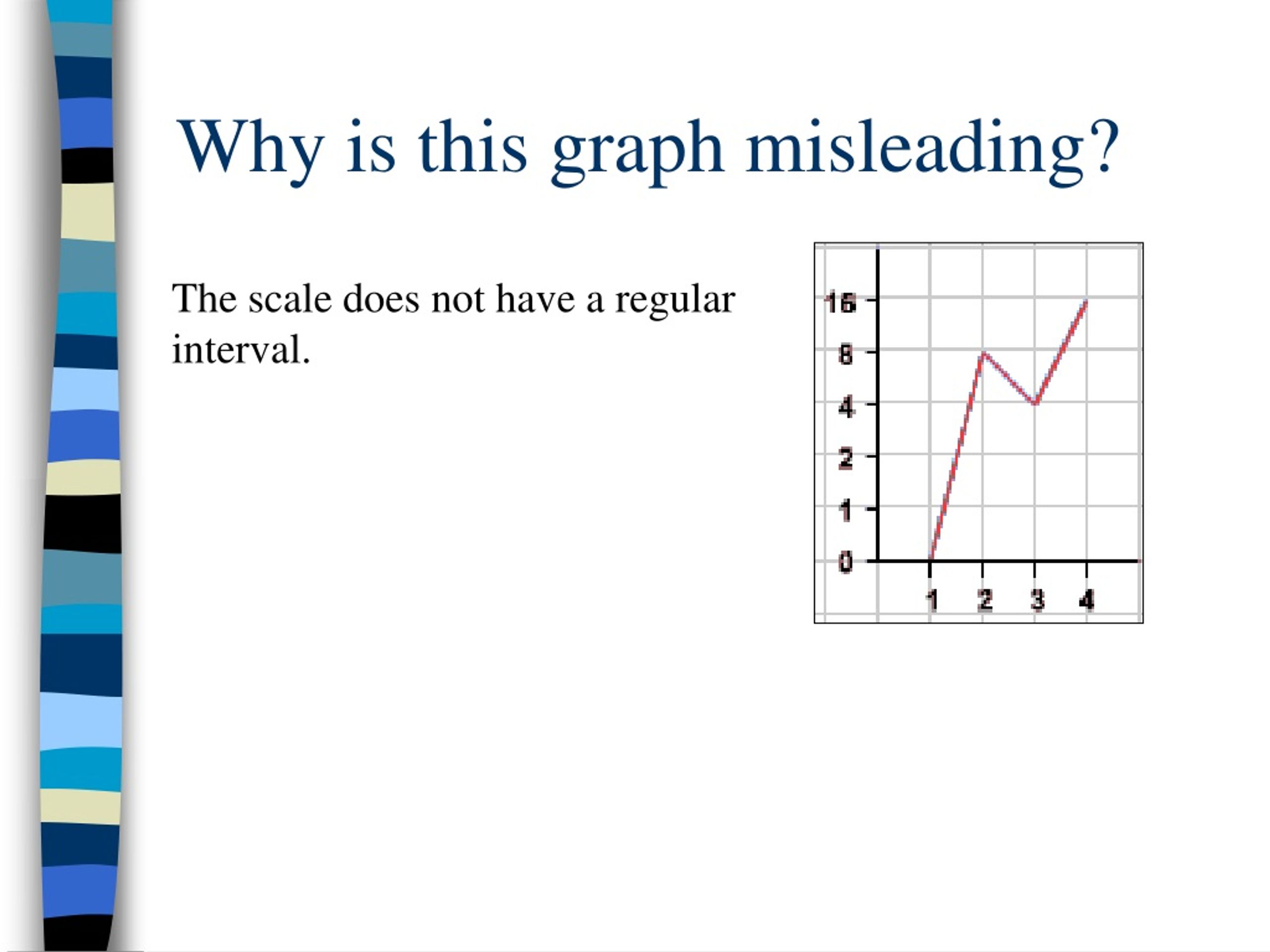
This overview discusses how graphs can distort information through scale manipulation, axis interval inconsistencies, and. First, analyze the graph to determine what could be misleading about the data presented. The scale on the horizontal axis may have the units unevenly spaced or the vertical axis may not start at 0 when recording frequency.